Hey there! Welcome!
Get updated on
Select Speciality
Top Picks
8 Jan, 26
The updated AHA statement expands on prior evidence, presenting new data that reinforce the link between periodontal disease and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease, while underscoring possible mechanisms and existing knowledge gaps.
6 Jan, 26
The 2025 ACC guidance highlights critical care in cardiogenic shock by recognizing the hemodynamic impact of PEEP on ventricular function, selecting invasive ventilation when instability warrants, and applying early structured interventions during the Golden Hour to support perfusion.
8 Jan, 26 Diabetes Ther.
Diabetes Ther.
- Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (MASH) worsened outcomes in a real-world cohort of adults with T2DM
- In 7396 microvascular & 6207 macrovascular matched pairs (mean follow-up 2.8 vs 2.4 yr), MASH increased hazards: microvascular complications; sHR: 1.19, macrovascular complications; sHR: 1.15
- Risks persisted across HbA1c (< or ≥7%) & age (< or ≥65)
- MASH accelerates T2DM-associated complications.
8 Jan, 26 Clin Microbiol Infec...
Clin Microbiol Infec...
- Systematic review/meta-analysis of 16 studies (≥60 yrs, n=1933 screened) assessed urine dipstick accuracy for bacteriuria/UTI
- Pooled sensitivity was high (90%) but specificity low (56%). In symptomatic older adults, sensitivity was 92% but specificity only 39%
- Findings showed dipsticks are inconclusive for UTI diagnosis in older adults, supporting discontinuation of their use.
7 Jan, 26 Indian J Ophthalmol.
Indian J Ophthalmol.
- A case series of 9 IA patients: 7 went to ophthalmologist for vision defects (age 58.9 y, 71% female)
- Symptoms: diplopia 57%, defective vision 43%, comorbidities in 43%
- Examination showed 3rd nerve palsy, 6th palsy (both 28.5%), RAPD/optic pallor (43%), hemianopia (14.2%); as per MRI: anterior aneurysm 100%, posterior 11%, multiple 28.5%; morphology: saccular 71.4%, fusiform 28.5%
- Early detection of IA is vital.
7 Jan, 26 Respir Med
Respir Med
- The study assessed whether early termination of the 6-minute walk test (6MWT) predicts poor outcomes in COPD
- Among 2,085 patients, 6.3% stopped early, showing worse lung function and higher symptom burden
- Early termination correlated with increased exacerbations, higher 3-year mortality, and prognostic value comparable to the BODE index, making it a practical marker for risk stratification.
6 Jan, 26
Featured

8 Jan, 26
24 Dec, 25
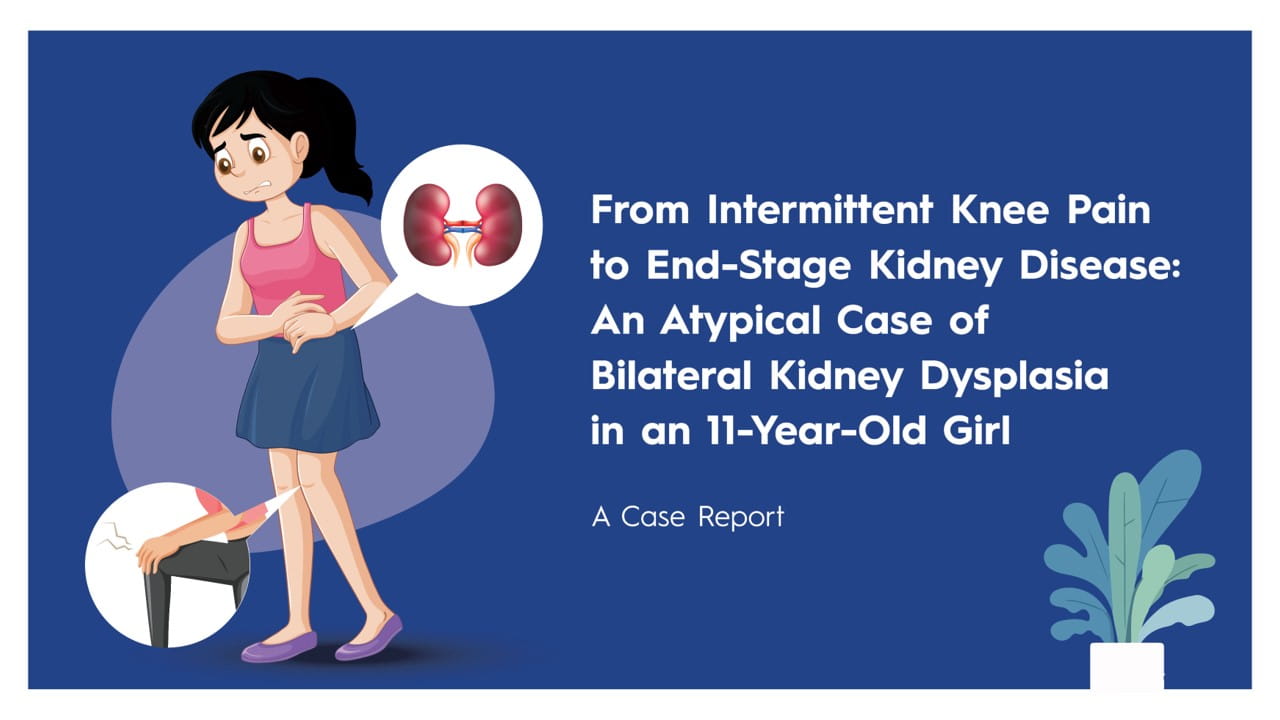
24 Dec, 25